Have you ever wondered about the precautions you need to take when using methylene blue?

This image is property of cdn.prod.website-files.com.
Understanding Methylene Blue
Methylene blue is a compound that has been around for a long time. Originally developed as a dye, it’s now widely used in various medical and scientific fields. It can treat conditions such as methemoglobinemia, a disorder in which the blood has an abnormal amount of methemoglobin, affecting the ability to carry oxygen. Beyond these medical areas, you might find it in aquariums or as an indicator in various experiments.
With its myriad applications, it’s crucial to understand not just how to use it but also what to avoid. Knowing this can help you navigate its use safely and effectively.
Interactions to Watch Out For
When you’re considering using methylene blue, it’s essential to pay attention to potential interactions with other substances. These interactions can skew results or even lead to adverse effects.
Other Medications
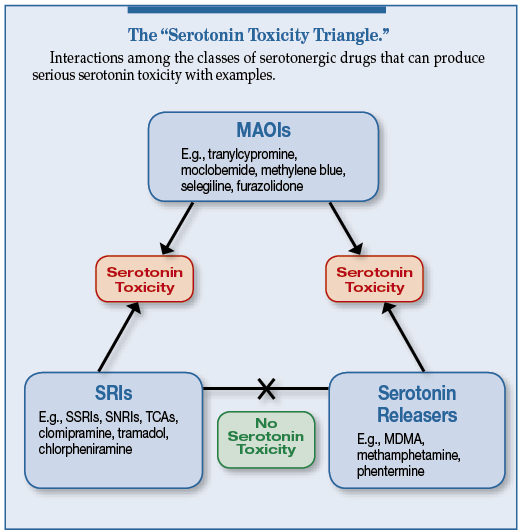
Methylene blue can interact with a range of other medications, which can amplify side effects or reduce effectiveness. For instance, it reacts with certain antidepressants, particularly those in the MAOI (monoamine oxidase inhibitor) category, such as phenelzine. This interaction can potentially lead to severe hypertension or a life-threatening condition known as serotonin syndrome.
Here’s a breakdown of some common types of medications to avoid:
| Medication Type | Example | Reason for Avoidance |
|---|---|---|
| MAOIs | Phenelzine | Risk of hypertensive crisis |
| SSRIs | Fluoxetine | Risk of serotonin syndrome |
| SNRIs | Venlafaxine | Risk of serotonin syndrome |
| Antipsychotics | Clozapine | Risk of increased side effects |
| Other Medications | Warfarin | Can affect blood clotting levels |
If you’re prescribed methylene blue, it’s vital to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re currently taking. They can help you manage any potential risks.
Alcohol
If you enjoy an occasional drink, consider how it could affect your use of methylene blue. Alcohol can enhance some of the side effects, like dizziness and confusion. Moreover, if you’re using methylene blue for a medical condition, drinking may complicate your symptoms or recovery process.
Supplements and Herbal Products
Don’t overlook the potential interactions with supplements and herbal products! Many people think they’re harmless, but ingredients like St. John’s Wort could interfere with the effectiveness of methylene blue. Always consult with a healthcare provider about what you’re taking.
Medical Conditions to Consider
Certain pre-existing medical conditions can complicate your relationship with methylene blue. Before using this compound, you should be aware of how your health may interact with it.
G6PD Deficiency
If you have glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, using methylene blue could pose severe risks. The drug can induce hemolytic anemia in individuals with this condition, leading to a breakdown of red blood cells.
If you’re unsure whether you have this deficiency, a healthcare provider can guide you on getting tested.
Liver or Kidney Impairment
Your liver and kidneys play essential roles in metabolizing and excreting substances. If you have any impairments in these organs, methylene blue may accumulate in your system, leading to toxicity. Symptoms of toxicity can include a blue discoloration of the skin and urine, confusion, and abdominal pain.
Before using methylene blue, it’s essential to discuss your liver and kidney health with your healthcare provider.
Dosage Considerations
Understanding the appropriate dosage is crucial to avoid complications. Taking too much can lead to toxicity, while taking too little may not provide the desired effects.
Recommended Dosages
For medical applications, doctors will usually prescribe specific dosages tailored to your condition. If you’re looking to self-administer methylene blue—whether it’s for a legitimate health reason or otherwise—make sure to consult a healthcare provider for guidance.
- Mild Cases of Methemoglobinemia: The typical dose ranges from 1-2 mg/kg administered intravenously.
- Severe Cases: Higher dosages might be required, given in increments until symptoms ameliorate.
Methods of Administration
Methylene blue can be administered in various ways—oral, intravenous, or even topical in some cases. The route often determines the dosage as well as its potential side effects. If your doctor has specified a route of administration, stick to that.

This image is property of macsenlab.com.
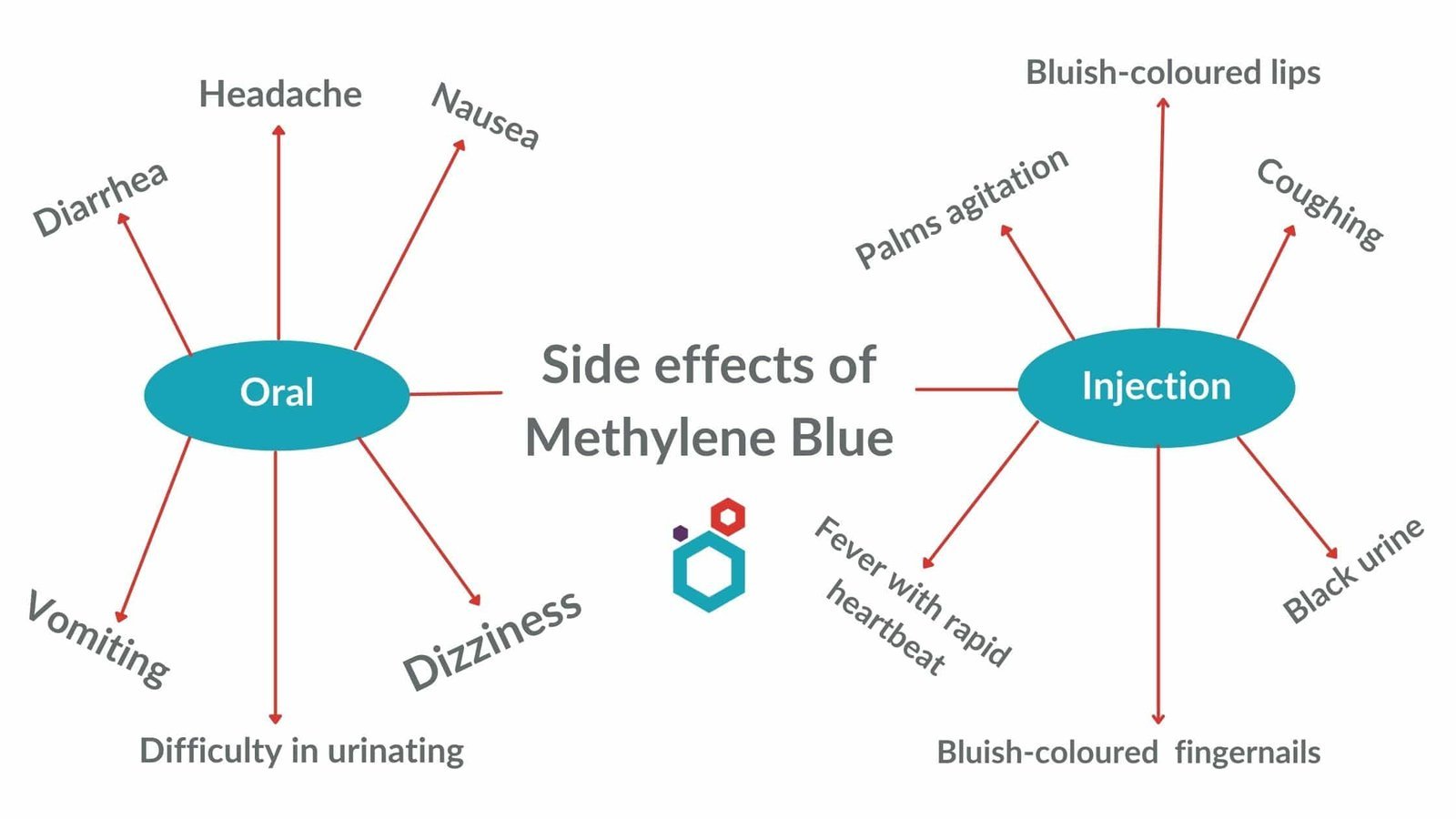
Side Effects and Reactions
As with any compound, methylene blue comes with its share of side effects. Being aware of them helps you understand what to look out for.
Common Side Effects
Here are some of the most commonly reported side effects:
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Blue Discoloration | This can affect your urine and possibly your skin, although it’s generally harmless. |
| Dizziness | You may feel lightheaded or a bit off-balance. |
| Nausea | Some people experience gastrointestinal upset. |
| Confusion | Especially if given in higher doses. |
If you notice any of these side effects, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider about adjusting your dosage or exploring alternative treatments.
Severe Reactions
In rare cases, methylene blue can lead to more severe reactions, which may include:
- Allergic reactions (hives, difficulty breathing)
- Severe headache
- Sudden increases in blood pressure
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Storage and Stability
Storing methylene blue properly is crucial for its efficacy. Improper storage can lead to degradation or contamination, rendering it less useful.
Recommended Storage Conditions
A high-level overview of how to store methylene blue includes:
| Storage Condition | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Store at room temperature (15-30°C) |
| Light Exposure | Keep away from direct sunlight |
| Moisture | Store in a dry environment |
Always check product labels for specific storage instructions, as they may provide additional details relevant to the specific formulation or concentration you have.
This image is property of www.apsf.org.
Alternatives to Methylene Blue
Maybe you’re considering the pros and cons of methylene blue and want to know what other options exist? Understanding alternatives can help you make informed decisions about your health.
Other Treatment Options
For conditions like methemoglobinemia, alternatives include:
- Ascorbic Acid: Vitamin C can help reduce methemoglobin levels in some mild cases.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: It delivers pure oxygen in a pressurized environment, which can help restore proper oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
Always work with healthcare providers to identify what’s best for your situation. They can evaluate alternatives based on your specific needs and conditions.
Conclusion
Navigating the use of methylene blue requires a keen awareness of what to avoid and the potential risks and benefits associated with it. Whether it’s understanding drug interactions, being mindful of specific medical conditions, or knowing how to store it properly, the information here helps you make safe and informed choices.
If you’re considering using methylene blue or already are, always consult a healthcare provider to guide you through the process. Though the compound has various benefits, it’s your health that ultimately matters most. Make informed decisions, and stay safe!

This image is property of global.discourse-cdn.com.