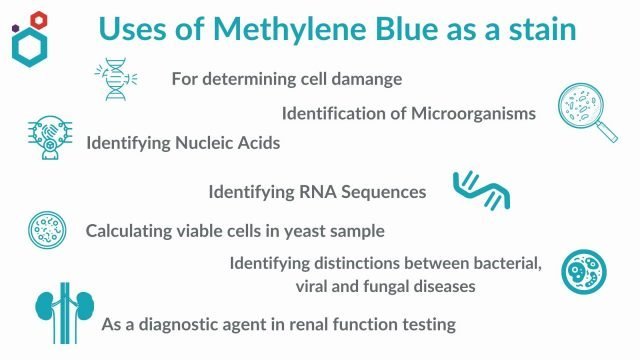
What if there was a colored dye that held the potential to treat various medical conditions? You might be surprised to learn about methylene blue. It’s not just a laboratory tool; it’s a compound with historical and contemporary applications in medicine. As we aim to unpack its uses, let’s consider how methylene blue can fit into the broader context of health and wellness.

This image is property of www.emnote.org.
What is Methylene Blue?
Methylene blue is a synthetic dye that was first created in 1876. Initially, it was used as a textile dye and later found its way into the world of medicine. It’s a small, blue, crystalline compound, and while it may look unassuming, its properties can be quite powerful.
One remarkable aspect of methylene blue is its role as a redox agent. This means it can accept and donate electrons, facilitating various biochemical reactions. The versatility in its chemical composition makes it useful in several medical settings—from treating infections to addressing conditions related to oxygen levels in the body.
Historical Context of Methylene Blue
Methylene blue has a rich history dating back over a century. It was first used to treat malaria, and for a while, it was considered a go-to remedy. You can imagine how revolutionary it must have felt then! However, as medical science progressed and more effective treatments emerged, methylene blue receded somewhat into the background, only to be rediscovered for a range of applications.
In the late 20th century, researchers began to take a renewed interest in methylene blue. Its potential therapeutic effects continued to astound researchers, particularly in its ability to act on various biological processes. This has led to a resurgence in the compound’s popularity, particularly in areas of research related to neuroprotection and antimicrobial activity.
Current Medical Applications of Methylene Blue
Today, methylene blue is employed in various medical capacities. Below, we’ll look at some of its most notable uses.
1. Treating Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia is a condition where hemoglobin—a protein in red blood cells—gets oxidized. Under normal circumstances, hemoglobin carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. When hemoglobin becomes methemoglobin, it can no longer effectively transport oxygen, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and even cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin).
Methylene blue serves as an antidote for methemoglobinemia. It acts by converting the methemoglobin back to its functional state, allowing oxygen transport to resume. The intravenous administration of methylene blue has shown to be particularly effective in acute cases.
2. Antiseptic Properties
If you’ve ever encountered a cut or wound that needs disinfecting, you might appreciate the history of methylene blue as an antiseptic. It has demonstrated antimicrobial activity against various pathogens. The dye can disrupt the cell membranes of bacteria, leading to decreased viability.
Interestingly, researchers have also investigated the use of methylene blue in treating infections associated with chronic wounds and even conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs). The challenge, however, lies in its specific concentration and delivery method.
3. Cognitive Enhancer
Methylene blue has attracted attention for its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. Some studies suggest that it may improve mitochondrial function and energy metabolism in cells. You might be asking, what does that mean for the brain?
Essentially, since your brain relies heavily on mitochondrial function for producing energy, a compound that enhances this process could improve cognitive performance. Some proponents claim that it may reduce cognitive decline and combat conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. However, it’s crucial to note that while promising, more research is needed in this area.
4. Cancer Treatment
In the realm of oncology, methylene blue has shown potential as an ancillary treatment. Its properties are being explored in photodynamic therapy, where it can be used as a photosensitizer that, when activated by specific wavelengths of light, generates reactive oxygen species to target cancerous cells.
While exciting, this area of research is still in relatively early stages. If you’re considering this in relation to cancer treatment, always consult with your healthcare professional for tailored advice and information.
5. Treatment for Psychiatric Disorders
Interestingly, methylene blue has also been studied for its effects on mood and anxiety disorders. Some studies indicate that it may affect pathways associated with mood regulation. While the results are not definitive, they suggest that there may be a role for methylene blue in treating conditions like depression.
As with any treatment, it’s essential to approach this option with caution and contextual understanding. It’s crucial to discuss any potential treatments with your healthcare provider.
How Methylene Blue Is Administered
The way you receive methylene blue will often depend on the condition it’s being used to treat. Here are some common administration routes:
Intravenous Injection
For conditions like methemoglobinemia, methylene blue is typically administered intravenously. This allows for immediate action, making it an efficient choice in emergency situations.
Oral Dosage
In certain contexts, oral administration may be appropriate. For instance, studies exploring methylene blue as a cognitive enhancer sometimes use oral dosages. However, the effectiveness can vary based on the specific condition and individual’s metabolism.
Topical Application
In cases of skin infections or wounds, methylene blue may also be applied topically. This method allows localized treatment, and again, the concentration will depend on the severity of the infection.

This image is property of macsenlab.com.
Side Effects and Contraindications
While methylene blue has several applications, it’s essential to recognize that it’s not without potential side effects. Here are some of the common ones you might encounter:
Common Side Effects
-
Skin Discoloration: One of the most noticeable effects is a bluish tint to the skin, urine, and even sclera (the white part of the eyes). This is generally harmless but can be alarming.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal issues, especially when taken orally, are reported by some individuals.
-
Dizziness and Headaches: You might experience dizziness since methylene blue can influence blood pressure and circulation.
Contraindications
There are specific populations that should avoid using methylene blue. These includes:
-
Individuals with G6PD Deficiency: This genetic disorder affects red blood cell function and can lead to hemolytic anemia with methylene blue use.
-
Pregnant and Nursing Women: There’s limited data on the effects during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so avoiding it unless absolutely necessary is generally advised.
-
Patients on Certain Medications: Methylene blue can interact with drugs like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which can lead to serious side effects like serotonin syndrome. Ensure you discuss all medications with your healthcare provider.
Regulatory Status and Research
What’s the current regulatory status of methylene blue? The compound is FDA-approved for treating methemoglobinemia. However, its other uses—like those for cognitive enhancement or mood disorders—don’t have the same level of regulatory approval. This means that while research is ongoing, these applications are not universally recognized or standardized.
Research Trends
Ongoing research continues to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and potential new beneficial uses for methylene blue. You may come across studies examining its role in neuroprotection, infectious diseases, and even metabolic conditions.
Always keep an eye on emerging literature—you might find groundbreaking studies that redefine how we understand methylene blue.
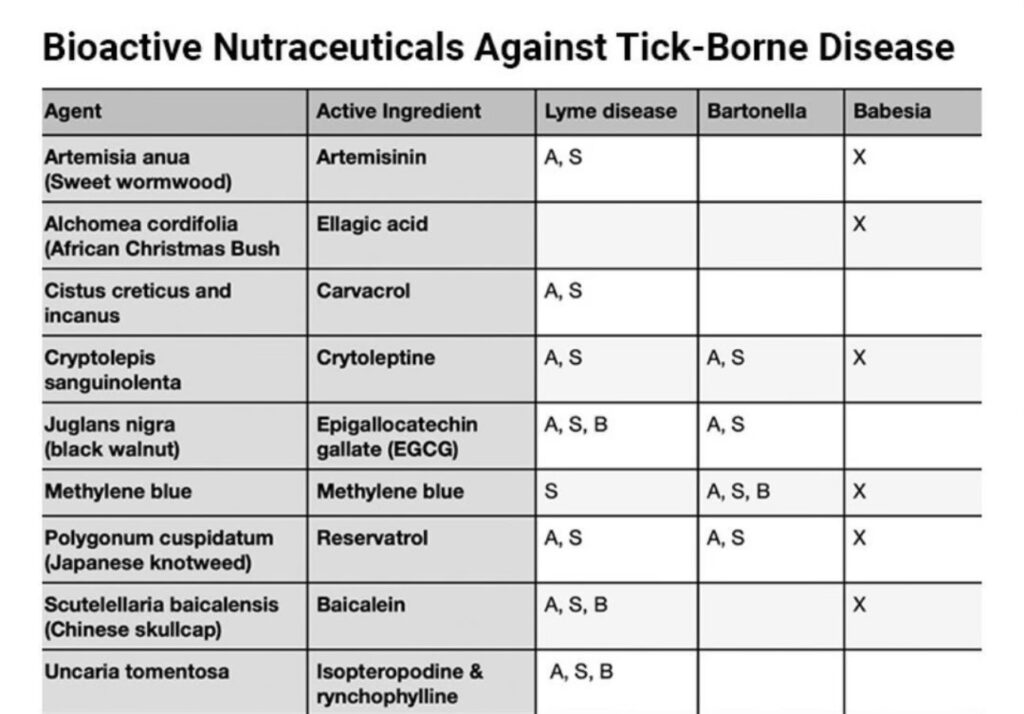
This image is property of projectlyme.org.
Conclusion: Understanding Methylene Blue’s Role
Methylene blue is so much more than a simple dye. From treating a specific blood condition to potential roles in psychiatric and cognitive health, it showcases versatility that deserves more attention in modern medicine. Given its historical significance and the promising avenues of research, it’s certainly a compound to watch.
That said, navigating any treatment requires diligence. It’s vital to have open conversations with your healthcare provider about whether methylene blue is appropriate for you, incorporating both its benefits and risks. By taking a thoughtful approach, you can better understand how methylene blue might play a role in your health journey.
Keep curious and informed about the treatments available to you, as understanding your options is a crucial step towards better health.